Sustainable Metal and Natural Materials Composite Filaments for 3D Printing
Key Information
AM Tech
Sustainble Reinforcement of Filament Industry
Manufacturing Potential Applications
- Extended durability and usability of furniture and household appliances
- Lightweight and durable components for automotives
Collaborators
NAMIC hub@SIT Problem Statement
- Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM)/Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is a popular and widely used 3D printing technology. However, thermoplastic-based materials such as ABS or PLA for printing do present a challenge regarding material properties and sustainability.
- The use of materials with limited mechanical properties presents a significant challenge to create products that last.
- Recycling discarded materials with a simple and effective solution that addresses the waste crisis while increasing the economic value of discarded materials.
Objective
- To investigate the potential of using reinforcement materials to enhance the mechanical properties of bio-based PLA polymer.
- To explore the possibility of improving the electrical and thermal properties of the polymer matrix by incorporating reinforcement materials.
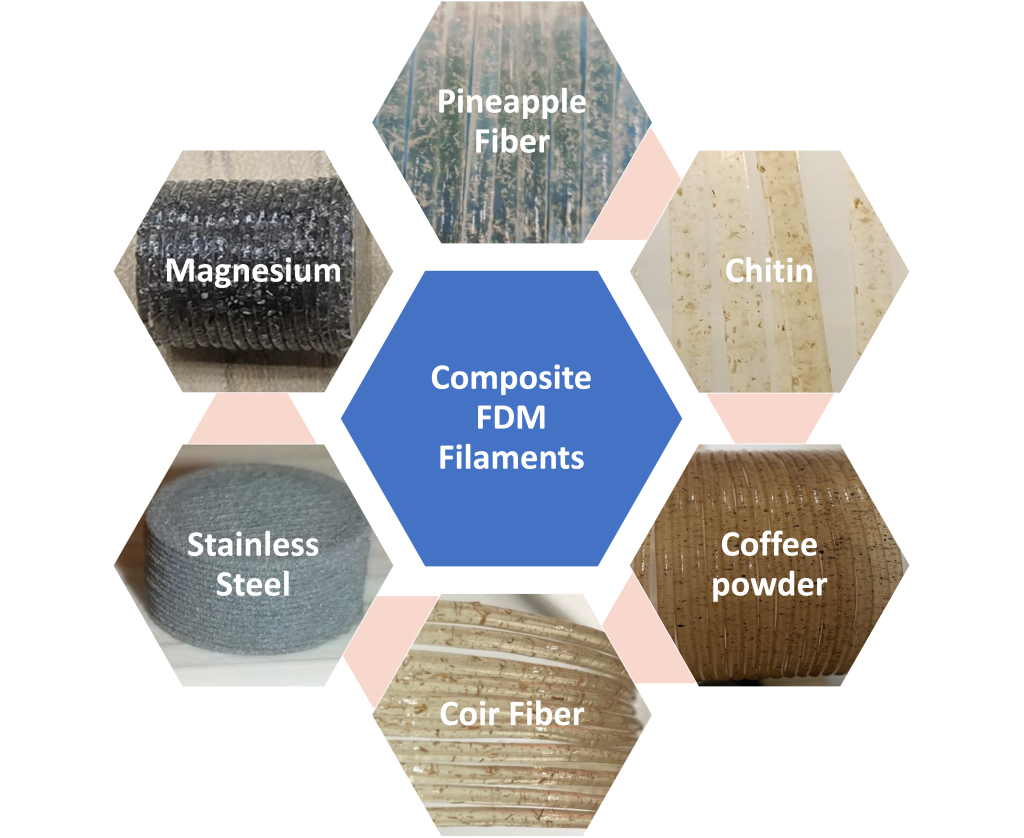
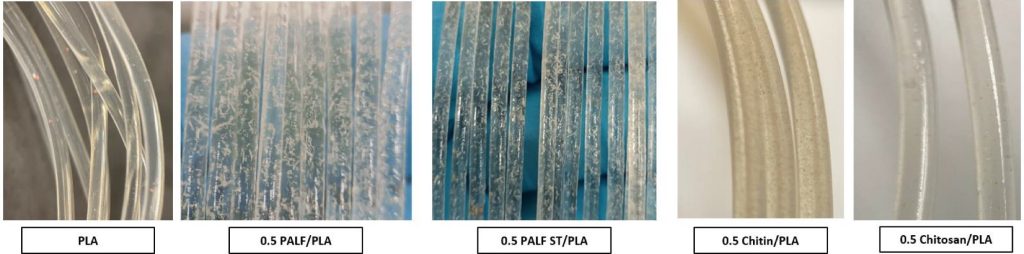
- To evaluate the effectiveness of metal powder and natural materials, such as Pineapple Leaf Fibre, Chitin, Chitosan, Coir Fibre and Waste Coffee Powder, as reinforcement materials for bio-based PLA polymer.
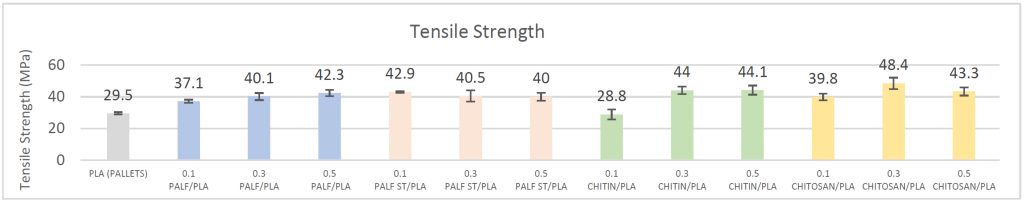
- To analyze the effect of different reinforcement materials on the tensile and flexural properties of the bio-based PLA polymer matrix.
Key Benefits/Outcomes
- Developing a new generation of sustainable filament with enhanced mechanical, electrical and thermal properties, using bio-based PLA polymer matrix reinforced with suitable natural and metal-based materials.
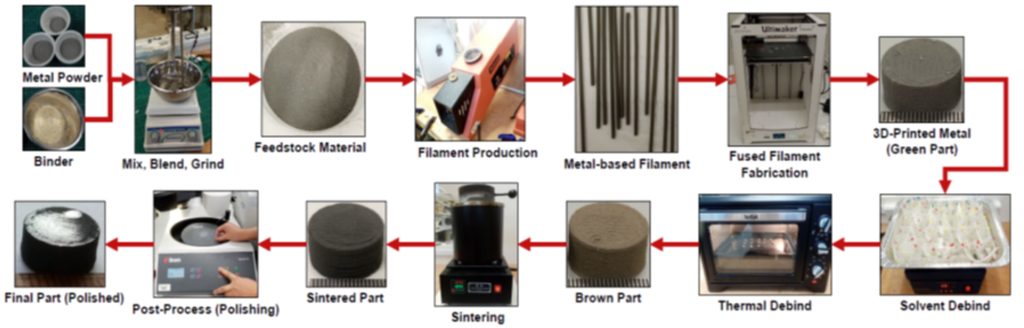
- Developing new methods for producing metal-based filaments suitable for FFF/FDM, using metal powders mixed with a removable binder or polymers such as PLA.
- Fabrication of dense metal parts or hybrid metal/polymer parts using the metal-based filaments produced through the developed methods.
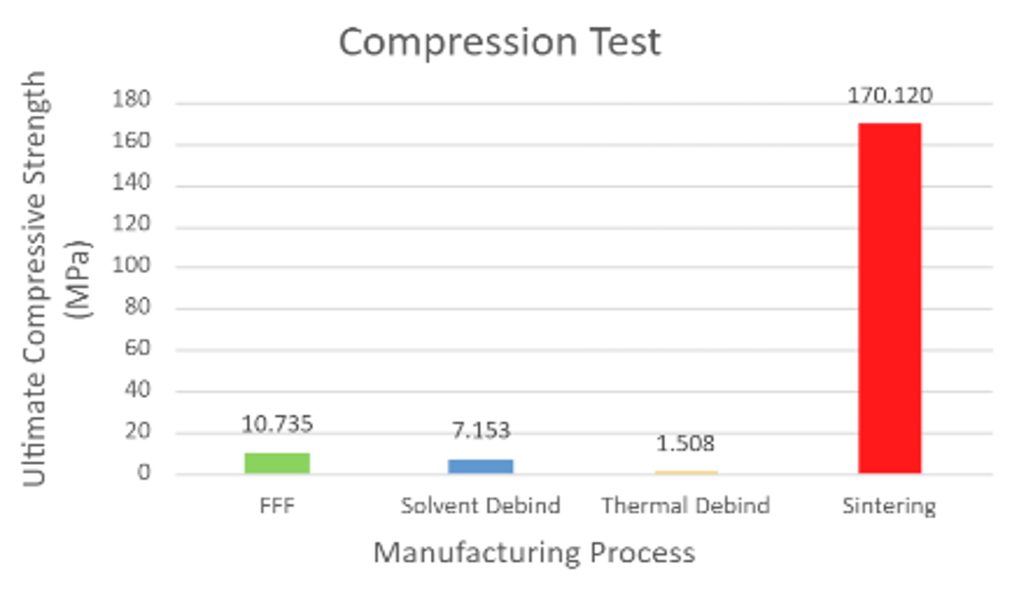
- Preliminary studies have demonstrated promising results for the densification of stainless steel samples, achieving 80% densification after sintering at 1090 degrees Celsius and ultimate compressive strength of approximately 170MPa.